Web-Based Automated Rainwater Storage and Water Quality Monitoring Design Using K-Nearest Neighbor Method
##plugins.themes.academic_pro.article.main##
Abstract
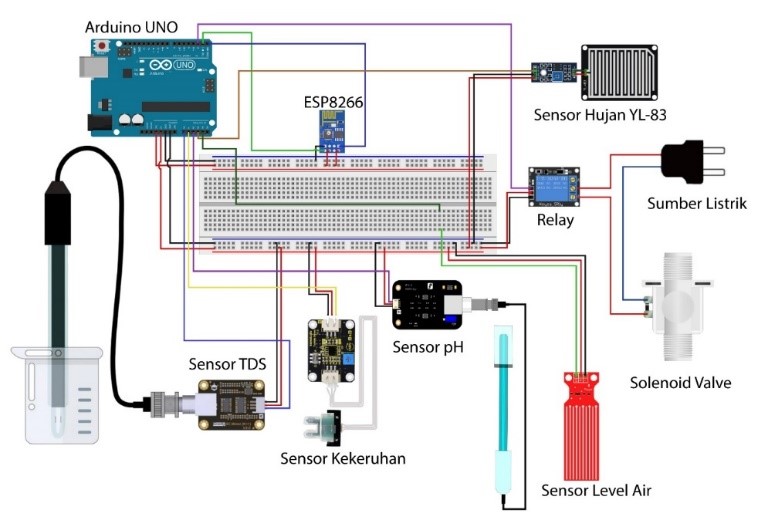
Clean water is a basic human need that is used for daily activities. However, as the population increases, the need for water also increases. One method of conserving water resources is Rainwater Storage. Conventional rainwater storage cannot be appropriately monitored, maintain water quality, and only works like a container, which, if left to continue, can result in the collected rainwater becoming a source of disease and dangerous for users. This research aims to create an automatic rainwater collection system and water quality monitoring that can control the flow of water that will enter the reservoir to keep the water entering the reservoir of good quality. In the manufacture of this system, three sensors are used, including a pH sensor, a water turbidity sensor, and a TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) sensor. In determining water quality, the k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) method is used to classify whether the water is feasible, less feasible, or not suitable for consumption. Data transmission uses the ESP8266 WiFi module, and monitoring data can be viewed on the website. Testing the system using an experimental method, and in testing, it is found that this system can classify water quality with an accuracy rate of 70%.
##plugins.themes.academic_pro.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
[2] T. Can, S. Larosa, and N. M. Putri, “OPTIMALISASI PEMANFAATAN AIR HUJAN DENGAN METODE PENAMPUNGAN AIR HUJAN ( PAH ) SEBAGAI ALTERNATIF PEMENUHAN KEBUTUHAN AIR BERSIH ( Studi Kasus : Kelurahan pandeyan , Kecamatan Umbulharjo , Kota Yogyakarta ) OPTIMIZATION OF RAIN WATER UTILIZATION BY RAIN W,†pp. 19–20, 2018, [Online]. Available: http://eprints.uty.ac.id/2111/
[3] H. Jatnika, M. F. Rifai, Y. S. Purwanto, and S. Karmila, "Smart System-Based Water Quality Measuring Device For Clean Water Availability," vol. 198, no. Issat, pp. 142–148, 2020, DOI: 10.2991/aer.k.201221.025.
[4] J. Bhatt and J. Patoliya, "IoT based water quality monitoring system 1,†no. 4, pp. 44–48, 2016.
[5] N. R. Moparthi, C. Mukesh, and P. Vidya Sagar, “Water quality monitoring system using IOT,†Proc. 4th IEEE Int. Conf. Adv. Electr. Electron. Information, Commun. Bio-Informatics, AEEICB 2018, vol. 6, no. 13, pp. 1–6, 2018, DOI: 10.1109/AEEICB.2018.8480963.
[6] A. Doni, C. MurthyMV, and M. Kurian, “Survey on Multi Sensor Based Air and Water Quality Monitoring Using IoT,†Indian J.Sci.Res, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 147–153, 2018.
[7] M. Batumalay and C. Batumalai, “Study and Implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) Based on Rainwater Sensor Using Arduino through Mobile Application,†vol. 2019, no. June 2019.
[8] H. Jatnika, M. F. Rifai, Y. S. Purwanto, and S. Karmila, Internet of Things: Mikrokontroler Arduino. Jakarta, Indonesia: Penerbit STT PLN, 2020.
[9] R. A. Arnomo, W. L. Y. Saptomo, and P. Harsadi, “Implementasi Algoritma K-Nearest Neighbor Untuk Identifikasi Kualitas Air (Studi Kasus : Pdam Kota Surakarta),†J. Teknol. Inf. dan Komun., vol. 6, no. 1, 2018, doi: 10.30646/tikomsin.v6i1.345.
[10] R. Rachmat, Y. H. Chrisnanto, F. R. Umbara, S. Informatika, U. Jenderal, and A. Yani, “Sistem Prediksi Mutu Air Di Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum Tirta Raharja Menggunakan K – Nearest Neighbors ( K – NN ),†pp. 189–193, 2020.